Priority Inversion
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_inversion
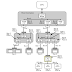
Consider there is a task L, with low priority. This task requires
resource R. Consider that L is running and it acquires resource R. Now,
there is another task H, with high priority. This task also requires
resource R. Consider H starts after L has acquired resource R. Now H has to wait until L relinquishes resource R.
Everything works as expected up to this point, but problems arise
when a new task M (which does not use R) starts with medium priority
during this time. Since R is still in use (by L), H cannot run. Since M
is the highest priority unblocked task, it will be scheduled before L.
Since L has been preempted by M, L cannot relinquish R. So M will run
till it is finished, then L will run - at least up to a point where it
can relinquish R - and then H will run. Thus, in above scenario, a task
with medium priority ran before a task with high priority, effectively
giving us a priority inversion.
Solution:
Disabling all interrupts to protect critical sections
A priority ceiling
Priority inheritance
Dead Lock
1. Mutual Exclusion: Only one process can use a resource at a given time.
2. Hold and Wait: Processes already holding a resource can request new ones.
3. No Preemption: One process cannot forcibly remove another process’ resource.
4. Circular Wait: Two or more processes form a circular chain where each process is waiting on another resource in the chain.
Preemption
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Preemption_%28computing%29
The period of time for which a process is allowed to run in a preemptive multitasking system is generally called the time slice, or quantum.
The scheduler is run once every time slice to choose the next process
to run. If the time slice is too short then the scheduler will consume
too much processing time.
An interrupt is scheduled to allow the operating system kernel
to switch between processes when their time slices expire, effectively
allowing the processor’s time to be shared between a number of tasks,
giving the illusion that it is dealing with these tasks simultaneously,
or concurrently. The operating system which controls such a design is
called a multi-tasking system
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Post Code on Blogger
Simplest way to post code to blogger for me: <pre style="background: #f0f0f0; border: 1px dashed #CCCCCC; color: black;overflow-x:...
-
Explain There is not interrupt PIN for PCIe interrupt. When device wants to raise an interrupt, an interrupt message is sent to host via ...
-
Configure Space Addressing One of the major improvements the PCI Local Bus had over other I/O architectures was its configuration mechanism...
-
What is LMA and VMA Every loadable or allocatable output section has two addresses. The first is the VMA, or virtual memory address. This ...

No comments:
Post a Comment